Batteries are our power-to-go, or at least that’s the promise that they deliver. Batteries give us the convenience of electricity, in a small portable handy form. The only problem is, most batteries tend to run flat very fast, unless you have a special charger, then they become garbage. Your wallet, and the environment both take a beating. Believe it or not, we throw away billions of batteries every year worldwide. The rechargeable batteries can definitely make a difference, and the best rechargeable batteries use a technology known as Lithium Ion.
Chances are, your laptop, your cellphone, or even your music playing device are using lithium ion. Lithium Ion batteries have been widespread since the early 90’s, but the chemistry of these batteries were invented by Gilbert Lewis, an American chemist (1875 – 1946), in 1912.
This is all very interesting stuff, but how do they work? Let’s take a closer look below.
Ordinary Battery Troubles
If you don’t know much about batteries, then I can tell you that they are basically canisters harboring chemical experiments. If you connect the two ends of a battery to a flashlight, then chemical reactions start happening.
The chemicals inside of the batteries will systematically split apart and join themselves with other chemicals, which produces Ions (Positively charged Particles) and electrons (Negatively Charged Particles).

Ions move through batteries, and electrons move through circuits to which the battery is connected. This provides electrical energy, causing your flashlight to light up. The only problem with batteries like this, is that there is one single reaction and they can only run in a single direction. This is the main reason why you can’t recharge your typical AA battery.
Reversible Reactions = Rechargeable Batteries
Rechargeable batteries use different chemicals that split apart in different ways than normal batteries. The main difference: rechargeable batteries use chemical reactions that are reversible.
When the battery is being used, the reactions go out one way releasing power, when the battery is absorbing power, the reactions move in the opposite direction.

The chemical reactions in rechargeable batteries can happen hundreds of times, and in both directions, which can typically give you anywhere between 2 – 10 years of battery life. (This depends on how well you take care of your battery, and the amount of use it gets).
How Do Lithium-Ion Batteries Work?
Like any other battery on the market, Lithium-Ion batteries are made up of compartments that generate power, otherwise known as cells.
Each cell is made up of three components: A negative electrode (This is connected to the (-) negative terminal), a positive electrode (This is connected to the (+) positive terminal), and an electrolyte, which is a chemical between the two electrodes.
The positively charged electrode is usually made from a compound known as lithium-cobalt oxide or LiCoO2. In newer batteries you may find the positive electrode made from Lithium Iron Phosphate or LiFePO4.
The negatively charged electrode is typically made from graphite (carbon) and the electrolyte used will often change from one type of battery to the next. Honestly, this isn’t wildly important when it comes to understanding how lithium batteries work.
Most lithium-ion batteries work the same way. When the battery is charging, the positive electrode, or lithium-cobalt oxide, gives up a portion of its lithium ions, which pass through the electrolyte to the graphite, or negative electrode and stay there.
During this process the batteries are taking in and storing energy. When the battery is discharging, the ions are passed back to the positive electrode through the electrolyte, which produces the energy to power the battery.
When charging and discharging, electrons are flowing in opposite directions from the ions around the outer circuit. The electrolyte does not carry electrons, it’s actually considered an insulator, or barrier for electrons.
As the Ions move through the electrolyte, and the electrons move in the opposite direction through the outer circuit, it’s imperative that both are working in tandem. If one of these processes stops, the other does as well.
If you don’t have ions moving through the electrolyte, then electrons are unable to move through the outer circuit, this can cause a loss of power. This also happens when you turn off your battery powered object. The electron flow is stopped causing the ions to stop flowing. This essentially stops the battery from discharging at a high rate, but not completely.
Even if your battery powered object is unplugged, the battery is still slowly discharging energy. Batteries tend to lose their juice when they sit for extended periods of time without use.
Unlike your typical battery, lithium batteries have built-in controllers that are electronic, which regulate charging and discharging. This can prevent overheating and overcharging, which may cause lithium-ion batteries to explode in certain situations.
Are Lithium Batteries for Golf Carts the Future?

Lithium-Ion batteries have been taking over the golf cart market since 2018, and honestly we aren’t surprised. Now, EZGO, Yamaha, and Club Car all offer their new carts equipped with Lithium batteries.
Of course you can still purchase any of their models with the traditional Lead Acid batteries, you’ll notice that they are slowly being phased out, possibly obsolete in the coming years.
So, should you switch to lithium? What makes these batteries better than the old Lead Acid Batteries that have been working for years? Unfortunately, every battery is not created equal, and in this section we’re going to do our best to explain why Lithium batteries are the future of golf cart power.
What Makes Golf Cart Lithium Batteries So Great?
In this section we explain to you the top 5 reasons you should consider Lithium Ion over the traditional Lead Acid battery.
1. Lithium Ion Batteries Charge Much Faster
The first thing we should touch on is the charging speed. The Lithium Ion battery is going to charge much faster than traditional batteries. For example, traditional Lead Acid Batteries will need a solid 8 hour charge when completely depleted.
Lithium Ion batteries are going to charge almost 80% of the battery in 1 hour, and can completely charge in 3 hours.
2. Lithium Ion Batteries Last Longer
Lithium Ion batteries are going to last you a lot longer than traditional Lead Acid. The chemistry used in Lithium Ion allows for more charge cycles.
You may notice that your lithium ion battery gets 3 to 5 thousand cycles in its life, where your traditional battery will only see 1,000 cycles max. That is pretty significant if you ask me.
3. Lithium Ion Batteries Reduce Overall Weight of Golf Carts
Lithium batteries are very light compared to traditional batteries. Lithium Ion batteries can weigh anywhere between 70 and 80 pounds. Traditional Lead Acid batteries can weigh up to 330 pounds!
If you convert your golf cart to lithium ion batteries, you could potentially lose almost 300 pounds of weight. This could increase ride height by a half an inch, and even help to increase battery efficiency.
4. Lithium Ion Batteries Require Little to No Maintenance!
If you are thinking you have to constantly watch water levels and continuously refill your batteries, think again. Lithium Ion batteries require zero water or filling, which means no more corrosion. This is a huge selling point for most businesses, venues, hotels, etc, considering all they have to do is plug them in for a charge and go.
Another massive difference between Lead Acid and L-I is the charge depletion over time. What happens if you don’t touch or start your golf cart for a month? The traditional battery is going to lose almost 35% of its charge if left sitting for a month.
A Lithium Ion battery on the other hand is only going to lose 3% of its charge in a month. So essentially you could leave your fully charged cart sitting in your garage for a year, and the battery will still be 75% charged. Pretty amazing stuff.
5. No Power Loss with Charge Loss
If you use a traditional Lead Acid battery, you’ve probably noticed how it can lose power the more you run it. As the batteries heat up and lose their charge, the power of the cart and the torque get lower as the battery charge depletes.
Lithium Ion batteries work on full power all the time, no matter how much charge is left. This is very similar to your phone. If you have 50% battery or 2% battery, that golf cart will have the same torque and power.
Converting your Golf Cart to Lithium Ion
If you think that changing over from traditional to lithium ion is difficult, you’re wrong, it’s actually super easy. All you have to do is pull out your old crusty batteries, drop in your new 12 volt Lithium Ion batteries, reconnect your wires, secure the batteries down, and you’re good to go.
Lithium Ion batteries also tend to be smaller than traditional Lead Acid, so you may find yourself with some extra room under the seats.
Are Lithium Ion Batteries for Golf Carts Expensive?
There is no way around this so i’m just going to say it. Lithium Ion Batteries are expensive. A lot more expensive? Well not that much more…
A standard pack of lithium ion batteries is going to cost you anywhere between $1,100 and $3,000. Sure this may seem like a lot, but honestly, it’s worth the money. These batteries are going to last you a lot longer, take less time to charge, and reduce the weight of your cart.
The Top Lithium Ion Batteries for your Golf Cart
There are a variety of major companies making quality lithium batteries for golf carts. It can be hard to choose from this huge selection, so we wanted to make things a little easier on you.
Below is a short list of the Lithium Ion Battery Companies that we trust, and that UPS and FedEX trust to ship to you!
- RELiON Lithium Ion Batteries
- Trojan Lithium Batteries
- Samsung Lithium Batteries
- Allied Lithium Batteries
Charging and Discharging Lithium-Ion Batteries
As the name suggests, lithium batteries work by the movements of lithium-ions. Ions are moving in one direction when the battery is being charged, and the opposite when supplying power. Let’s take a closer look at how these two processes work.
- When charging, the lithium-ions (GREEN Circles) flow from the positive electrode (RED) to the negative electrode (BLACK) through electrolyte (WHITE/GRAY). Electrons flow from the positive electrode to the negative electrode, but take a longer route around the outer circuit. The lithium is deposited from the negative electrode, which is where the ions and electrons meet.
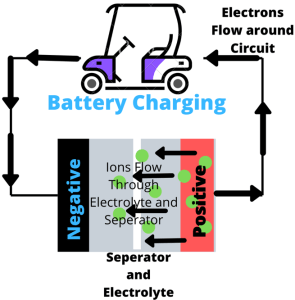
- When the ions are no longer flowing, then the battery is charged, and ready to use.

- When discharging, the ions are sent back through the electrolyte from the negative to the positive electrode. The electrons also flow in the outer circuit from the negative electrode to positive electrode, powering your device. When the electrons and ions combine at the positive terminal, the lithium is deposited.

- When the ions are done moving back, the power source is completely discharged, and will need to be charged again.

Storing Lithium-Ions
The picture below shows a little bit more detail about what’s happening in the battery. The negative electrode, or graphite is pictured in black on the left, while the positive electrode, or cobalt-oxide, is pictured on the right in red. The ions are represented by green circles.
When a battery is charged the lithium-ions are packed, and stored in between atom thick sheets of carbon known as graphene inside the graphite electrode (All of the ions have moved to the left). The completely charged state is basically layers of lithium-ions upon graphene.

As the battery power is depleted the lithium-ions move back from the negative electrode to the positive electrode (left to right). When the battery is completely discharged you once again have layers of lithium ions stacked this time with cobalt ions (red) and oxide ions (orange). When the battery is being charged or used, the lithium-ions are being shot back and forth between each electrode.

The Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries
Generally speaking, lithium-ion batteries are a lot more reliable than the older battery technology such as “nicad” or nickel-cadmium.
You never have to worry about Lithium-ion batteries suffering from the “memory effect” This is essentially a problem Nicad batteries have when they aren’t fully discharged (battery becomes harder to charge over time if you don’t fully discharge battery).
Beyond that, Lithium ion batteries contain no cadmium (heavy toxic metal), so you could say they are better for the environment, though dumping any plastics or metals into landfills is never good.

Compared to your heavy rechargeable batteries such as car batteries (lead acid), Lithium-ion batteries are quite light considering the amount of energy and power they can store.
In summary, Lithium-ion advantages include…
- Easy charging, No “memory effect”
- Powerful for a Lightweight battery
- Contain no heavy toxic metals
The Disadvantages of Lithium ion Batteries
To be honest, if I’m going to explain the lithium battery drawbacks, it’s important to understand what exactly I’m comparing them to. If we’re talking about a power source for cars, then they should be compared to gasoline, not other types of batteries.
Even though we have made some pretty crazy advancements over the years, kilo for kilo, batteries are only able to store a fraction of the energy produced by gas. To be more specific, batteries have a much lower energy density, aka they store less energy in each unit of weight.
You can also use this to argue the fact that it takes minutes to fill your gas tank, but hours to recharge your battery.
Don’t get me wrong, these slight disadvantages are balanced out by advantages, such as zero air pollution (No emissions from exhaust or tailpipe), and much greater fuel economy.
Let’s leave aside cars for a moment, and go through the problems you may experience with lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium Ion Issues
The first, and probably the biggest issue that lithium-ion batteries have is their safety. Lithium batteries tend to catch fire if they experience an internal malfunction (short circuit), or if they are overcharged. In both cases, this is what is considered a “thermal runaway”, which eventually causes the battery to explode, or at the least catch fire.

If Lithium-ion batteries aren’t ventilated correctly, they can swell up with gas, as seen above.
You can easily solve this problem by installing a CID or current interrupt device, which is an internal circuit breaker designed to kill the current charging the battery if the voltage reaches its maximum point, or if the internal temperature gets too hot.
Sure concerns remain, and in 2016 the ICAO (The International Civil Aviation Organization) prohibited shipments of lithium batteries on planes carrying passengers, because of the potential dangers.
Yes Lithium-ion batteries have gained quite the attention over the years, with fires breaking out in planes and electric vehicles, but you should keep in mind how little this actually happens, considering how common this technology actually is. Lithium-ion batteries are in everything from phones, to laptops, and other handheld gadgets.
Again, yes there are risks of fire with lithium-ion batteries, but gasoline in cars catch fire a lot more often, which causes real explosions! To be blunt, fire isn’t a new problem only caused by lithium-ion battery technology.
How can we solve this problem? Well, according to Ionic Materials, they may have a solution. Using flame resistant polymers, instead of the very flammable electrolytes that are typically found in lithium-ion batteries.
Another option proposed by John Goodenough, the chemist behind bringing lithium-ion batteries to the world, suggests using “doped” glass (made electrically conductive) for the electrolyte. I guess only time will tell whether or not one of these options, or something else completely, topples the lithium ion battery from its podium of best rechargeable battery in the world.
In summary, Lithium batteries disadvantages include…
- Fraction of power per weight compared to gas
- Possibility of fires or explosions if overcharged or overheated
- Can take hours to charge
Who Invented Lithium-Ion Batteries?
In 1970, at Oxford University, the helpful handy lithium-ion power packs were officially pioneered.
John Goodenough and his amazing colleagues Koichi Mizushima, Phil Jones, and Phil Wiseman had their research published in 1980, which was turned into a commercial technology by the well known company Sony, who brought the world the first lithium-ion battery in the early 90’s.

Since then, the technology has become extremely common, as we produce nearly 5 billion each year, most of which come from China. Last year (2019) John Goodenough and his collegues Akira Yoshino, and Stanely Whittingham shared the Chemistry Nobel Prize for their groundbreaking technology.
In Conclusion
Lithium-ion batteries are a technology that has been around, is being used, and will only get better in the future.
Above, you learned that Lithium batteries are the most common rechargeable battery on the market. They provide an ample amount of power for handheld devices, golf carts, and even electric cars.
You learned how lithium-ion batteries work, and the process they use to discharge and charge. You also learned the advantages and disadvantages to lithium batteries such as how easy they are to charge, and how lightweight they can be considering the power they produce.
We also explained the problems you may face with a lithium ion battery such as issues with overheating, and possible explosions.
I hope that this article has given you a better idea on how Lithium batteries work, and why their technology is such an important part of our daily lives.
If you have any questions regarding lithium-ion batteries, or you have experience using a lithium ion battery in your golf cart, let us know in the comments below! Thanks for reading







